Your Complete 2023-24 MEDDIC / MEDDICC Sales Process Checklist
What is MEDDICC?
MEDDICC is a sales qualification methodology which stands for Metrics, Economic Buyer, Decision Criteria, Decision Process, Identify Pain, Champion and Competition.
Why Use MEDDICC?
There’s no doubt, the MEDDICC sales process has helped many sales teams and sales reps around the globe achieve extraordinary results. Statistics show that 30%+ growth rates in saturated markets and 250%+ in start-ups are possible. In fact, many sales reps that touch MEDDICC will never work without it again.
Fast-paced companies like Workiva, MongoDB, Alfresco, Snowflake and many more have built a healthy pipeline and forecast on the fundamentals of MEDDICC.
Read on to get a brief overview of this simple and lightweight qualification process, and how you can implement MEDDICC on Salesforce.
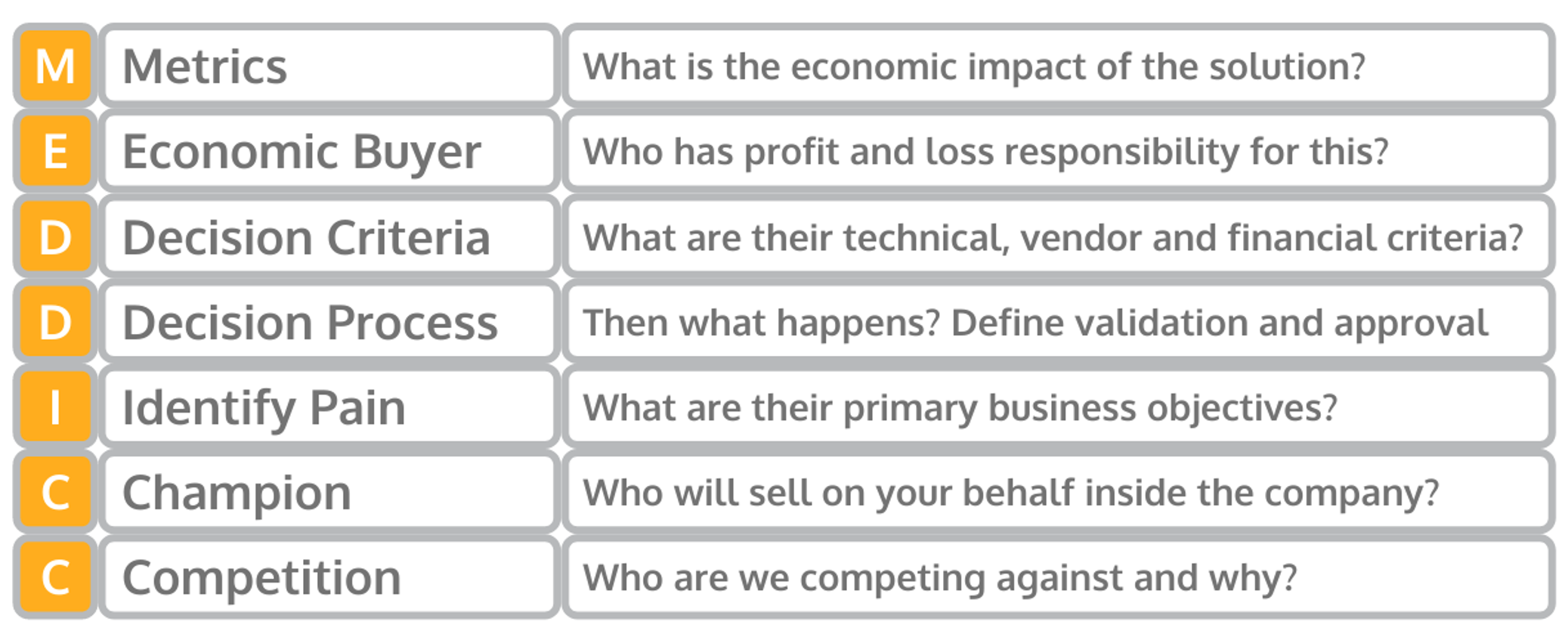
Here’s the basic MEDDICC sales process checklist:
| MEDDIC Qualifiers | Explanation | |
|---|---|---|
| M | Metrics | What is the economic impact of the solution? |
| E | Economic Buyer | Who has profit and loss responsibility for this? |
| D | Decision Criteria | What are their technical, vendor and financial criteria? |
| D | Decision Process | Then what happens? Define validation and approval? |
| I | Identify Pain | What are their primary business objectives? |
| C | Champion | Who will sell on your behalf? |
| C | Competition | Who are we competing against and why? |
MEDDICC Sales Process Qualifiers
Metrics
Metrics are quantifiable and measurable results that potential customers perceive as valid for his project or initiative. It can be divided in 2 major groups:
Below the Line
For example, cost savings and efficiency gains. Many times paired with reductions on FTEs (Full Time Equivalent).
Above the Line
These are more business-centric like increases in revenue or profit, quicker time to market, higher quality and customer satisfaction. These metrics are used to make decisions and build Business Cases or ROI.
Strong Metrics: We are 15 FTE (Full time equivalent) with 95% utilization. We are expanding our infrastructure 15% a year and we expect another acquisition this year, which will double. We will not get a budget to increase FTEs.
Questions to ask:
- How would you measure the success of your project?
- Which metrics around cost, efficiency or business do you need to achieve?
- How would this success be measured by the business?
Note: Collecting these metrics from your existing clients makes wonderful proof points on your discovery calls with prospects.

Economic Buyer
The Economic Buyer is a person with the discretionary approval to spend. Economic Buyers are decision makers who give the ultimate “yes” or “no” to a project. Usually, the person has a clear sight on the business benefits, decision criteria and the process to close a deal.
Meeting the real Economic Buyer, checking for his sponsorship, criteria and next steps usually sheds a lot of light on the complex decision criteria and processes. Preparing the Economic Buyer meeting is key to success, however you need to do your homework on the value proposition and earn the right to ask for this meeting.
Qualifying if you talked to the real Economic Buyer is key. A good qualifying question could be: ”If you & I come to an agreement, is there anybody else formally or informally that would need to be involved or approve?”
Questions to ask the Economic Buyer:
- Do you sponsor the project?
- What does success look like for you?
- What are the next steps, if we fulfil the success criteria?
If the Economic Buyer confirms the project and outlines a possible close date, your deal has a good chance of closing. If you do not meet the Economic Buyer or get his approval, your chance of closing a deal in time drops below 50%.

Decision Criteria (Dc)
Every project has a formally or informally defined decision criteria. These are often categorized further as Technical, Commercial and Legal Decision Criteria.
Technical decision criteria (TDC)
Here, we talk about the criteria to understand the feasibility. Are the use cases covered by the potential solution? Does it comply with the existing infrastructure and, if so, how does integrate?
How easy is it to work with and does it fulfil the standards of the Enterprise Architecture?
Typically this TDC will be validated in a Proof of Concept or some sort of Technical Decision Making Process.
Business/Commercial Decision Criteria (BDC)
The most common BDC is Alignment to Budget. However, corporations are very much driven by Return on Investment nowadays – sometimes in less than 12 months to justify the investment.
Furthermore, there are different types of budgets like capital expense (CAPEX) or operation expense (OPEX). Some clients have huge OPEX reduction campaigns or have certain cash-flow requirements that drive the decision criteria.
Thoroughly understanding and aligning yourself to the clients’ needs to establish a good fit will show great flexibility. This can influence the decision towards your offering.
Questions to ask:
- What are the technical criteria to make a decision?
- How do you calculate the ROI for this project to justify the investment?

Decision Process (Dp)
While the decision criteria are all about what the decision is based upon, the Decision Process is about the route to it.
We primarily separate this process into the route to a technical decision (Technical Decision Making), the route to money (Business Decision Making) and the route to paper (Paper Process).
Technical Decision Making (TDM)
Based on the TDC, companies set up formal or informal processes that lead to a technical decision. It is important to understand what these steps are and who is involved in it.
As the decision criteria, this process should also be documented and confirmed by the client.
Business Decision Making (BDM)
Who needs to approve? Are there any formal boards? Is there a formal procedure or a paper process involved in a project approval workflow? How long does this usually take?
Paper Process (PP)
Rigorous regulatory or business compliance needs often lead to time intensive negotiations. These can take weeks or even months, but are necessary to have a legal agreement.
This process is the No. 1 reason why contracts get postponed and deals slip out of a quarter. Make sure you have executive sponsorship to give negotiations with Purchasing and Legal the right focus, the right time and the right resources. Be paranoid about the details!
Questions to ask:
- Which personnel are involved and what are the steps to reach the decision?
- How is this put in sequential order and which timeline is it based on?
- How does the approval process look like for $100K, $500K or $1 million?
- Paper process: How is the legal construct set up? Are there frame agreements in place? What are the critical mandatory terms and conditions? Which contractual paperwork is the basis of negotiation?

Identify Pain
Together with the Champion, the Pain is one of the 2 major qualifiers in the discovery phase that are required in order to understand if you have an opportunity.
A strong pain can be a technical or business shortage that the client would like to overcome, stop or change.
It must impact the customer in terms of time, cost, risk or revenue, if not solved within a certain time frame.
We call it “the consequence of doing nothing when the compelling event takes place.”
Important: A weak pain or unclear consequences will usually cause delays or reduced budgets due to the lack of priority for the executive management!
Example of a strong pain:
- ABC Soft needs to deliver a solution by the end of the year. They have major delays caused by serious bugs, which may prevent an on-time delivery. (Pain)
- There is a penalty clause of $100K per week if the software is not up and running on January 1st. (Implication/Consequence: Cost->strong, Reputation-medium)
Example of a weak pain:
ABC Soft needs to have a regression testing due to buggy software.
What info is missing here?
Questions to ask:
- Pain: What causes the delays?
- Implication: What does this mean for you and the company?
- Is it really compelling: What is the consequence of doing nothing? Does it impact your business?

Champion
Pain is an important driver and implication drives urgency.
However there is always an owner with a personal interest to get this pain solved. This personal interest drives the person to collaborate with peers, consultants and vendors to attack the pain as soon as possible, speeding up the buying process.
The goal should be to identify these individuals. Even if they don’t carry the official management head, they can be spotted as they are well accepted by their peers, are very influential and usually have a good track record of successful projects that make them visible in the chain-of-command.
Once you identify the goals of your potential Champions, you will be able to develop the relationship by enabling him to address the pain, i.e. linking them to the subject matter experts in your company, inviting him/her to the right seminars or linking them up with your references so they can learn from their experiences in handling projects like his.
Once you’ve built up a real Champion, he will recognize your support and understand that you will be able to help him solve the pain moving forward. It will become a joint effort and your Champion will become a true defender of the cause, selling on your behalf whenever you’re not around.
Questions to ask:
- Why is this person a champion?
- Does this person have the influence?
- What is his/her personal interest?
- Will he/her stand up for you and sell for you when you are not there?

Competition
Competition is one of the most neglected and underestimated risk factors when it comes to securing and closing a deal. Even if your prospect assures you that he or she is not looking into other solutions, it could still be that the approvers will ask for comparisons or purchasing will request to get additional quotes for price comparison’s sake.
Moreover, competition could go beyond a solution that’s offered by another company. It could also refer to the client’s “Do It Yourself (DIY)” solution or current way of doing things. Ie. The “if it ain’t broken why fix it” mentality where they decide to do nothing and continue with the status quo.
You really do not want to find out that you’ve been competing with another solution only after losing the deal.
Questions to Ask:
- Who are we competing against?
- Why are we competing against them?
- Could they do nothing?
- Are they adopting an open Source/DIY approach?
- Who in the account is championing your competition?
- Do we know who else needs to be involved?
Knowing your competition inside out will help you strengthen your case to neutralize your enemies early in your sales process. Identifying and building multiple champions will allow you to grow deeper roots within your prospect’s organization and gain more access to information. Doing so will also enable you to better understand the needs of the organization, so that you can set traps for your competitors and convince your prospect that your solution is the only solution that they will need.

After raising my close rate to over 90%, MEDDICC proved itself as a winning methodology.
Implementing MEDDICC on Salesforce
You can easily follow your MEDDICC sales process directly on Salesforce to manage all your opportunities – without having to rely on Word docs and spreadsheets.
Designed specifically for the B2B complex sale, iSEEit is the first Opportunity Management Tool to have MEDDICC right out of the box.






Super clear article. Very well written ?.
It’s great to see the Paper Process called out inside of the Decision Process.
Здравствуйте всем!
Рассчитываю поделиться важной информацией для всех, те, кто интересуется современными технологиями. Обзор по ссылке публикует наиболее полные и актуальные обзоры о умных лампочках и их преимуществах.
Who Our Device is For: Whom We Will Help
The vibration balancing and analysis devices from Vibromera are intended for various specialists and industries dealing with the upkeep of optimal performance in rotating machinery.
This includes various types of machines and mechanisms, from industrial fans, pumps, and compressors to complex turbomachinery and automotive engines.
Let’s explore the primary categories of users and applications where our device will be an essential tool.
Dynamic balancing addresses imbalances in rotating objects across multiple planes. This advanced technique involves high-precision measurements and corrections, ensuring smooth operation, increased energy efficiency, and reduced wear on critical components.
Production and Repair Companies
The main target for our devices includes companies involved in the manufacturing, maintenance, and repair of different types of rotating equipment.
This group encompasses manufacturers and service centers that focus on pumps, fans, electric motors, turbines, and other machinery.
Our device enables precision dynamic balancing on site, greatly simplifying maintenance and boosting production efficiency.
Research and Educational Institutions
Our devices are also employed for scientific and educational purposes, conducting experiments, researching vibrations and dynamics of rotating mechanisms, and training students and engineers in the basics of balancing and vibration analysis.
Your blog is a goldmine of information Regards from Pasang Iklan Properti Gratis
Hansell, Saul (October 27, 1993).
On 6 October 2008, BNP took over 75 of troubled financial institution Fortis’ actions in Belgium, and 66 in Luxembourg, in exchange for the Belgian authorities changing into the new group’s main shareholder.
Since 1945, governing through a single-get together authorities has occurred twice: 1966-1970 (ÖVP) and 1970-1983 (SPÖ).
A 2013 settlement between the police officers’ union and the county was criticized by NIFA.
I’m thoroughly impressed by this article. The clarity of your explanations and the depth of your insights are remarkable. Your ability to make complex topics accessible and engaging is truly commendable. Thank you for such an exceptional read. Best regards, Pasang Iklan Properti Gratis
Meninggalkan komentar untuk menjadikannya viral, terima kasih dari IDProperti.com | Pasang Iklan Properti Gratis